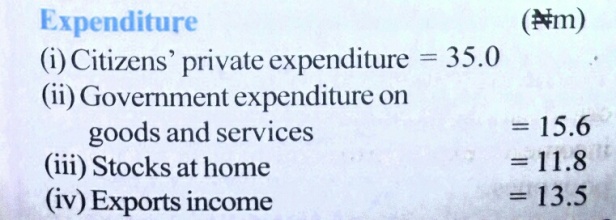Welcome! Our Economics lessons Continues! Do have a great moment studying with us!
Lesson Note
Subject: Economics
Topic: Elements of National Income Accounting
Lesson Objectives: At the end of the lesson, learners should be able to;
i. Explain the term National income
ii. List and explain the various types of National Income concepts
iii. State the factors the determines the National Income of a country
iv. Describe the methods of measuring the National Income of a country
v. State the reasons why National Income is measured
vi. List and explain the problems that are encountered while measuring and computing National Income
vii. State the uses of National Income
viii. List and explain the limitations of the usefulness of National Income statistics
ix. Define cost of living
x. Define standard of living
xi. Examine the relationship between cost of living and standard of living.
Discussions
National income accounting may be defined as the ways or means of computing or determining the money value of the total volume of goods and services produced or the total income earned in a given country over a period of time, usually a year.
The total income earned in a given country refers to the combination of income of individuals, business organisations and the government. As individuals and corporate bodies keep records of accounts, so do the government of various countries. A proper accounting system will reveal the standard of the economic life of a nation and these calculations give direction to economic progress of such nations.
Major National Income Concepts
i. Gross domestic product (GDP): Gross domestic product (GDP) may be defined as the total money value of all the goods and services produced in a country at a particular period of time but excluding net income from abroad. In calculating the GDP, emphasis is on earnings from citizens and foreign investment within the country. Earnings of citizens and their investments abroad are excluded from GDP. GDP is used to measure the rate of growth of the economy.
ii. Gross National Product (GNP): Gross national product may be defined as the total money value of all the goods and services produced in a country in a year plus the net income from abroad.
GNP takes care of the total money value of all the goods and services produced by the citizens of a given country. It excludes the contributions of foreigners to the GDP and includes the earnings of the citizens of a given country residing abroad. Mathematically,
GNP = GDP + Net income from abroad
iii. Net National Product (NNP): Net national product may be defined as the money of the total volume of production; i.e the gross product after allowance has been made for depreciation. In other words, the net national product is the gross national product less the estimated amount of depreciation or capital consumed during the year. Mathematically,
NNP = GNP – Depreciation
iv. National Income (NI): National income may be defined as the money value of the total volume of goods and services produced or the total income earned in a given country over a period of time, usually a year.
National income is the total of all the income obtained from economic activities during a specified period, usually one year, after allowance has been made for capital consumption.
v. Personal Income: Personal income may be defined as the income or amount of money received by individuals or households over a given period of time.
vi. Per capita income: Per capita income also called income per capital, may be defined as the average income of the individual in a given period of time, usually a year. Per capita income can be obtained by dividing the national income by the population of the country in that year. For example, per capita income for the year 1995 is:
Per capita income = National income for 1995
Population for 1995
Per capita income serves as an economic indicator of the level of standard of living and development.
vii. Real income: Real income may be defined as money in terms of goods and services it will buy. Real income is the national income expressed in terms of general level of prices.
viii. Disposable income: Disposable income may be defined as the income or amount of money that is left to an individual or household for spending and savings after the deduction of personal income taxes.
When taxes are deducted from an individual’s personal income, what is left is disposable income, which can be spent or saved by the individual or household concerned.
Factors that Determine the National Income of a Country
i. Availability of natural resources: A country with abundance of natural resources will experience increase in natural income than a country with little or no natural resources.
ii. Level of technology: A higher technological development will improve or increase a national income.
iii. Industrial development: Industrialisation also influences national income. The presence of industries or increased industrial activities can contribute positively to national income.
iv. Working Population: A country with a high working population is likely to increase national income than a country with a little population.
v. Economic activities: The economic situation of a country can influence the national income. While economic stability promotes or increases national income, economic instability decreases it.
vi. Nature of factors of production: The availability of the factors of production such as capital, labour, land and entrepreneur will enhance the national income of a country.
vii. Political situation: Political stability in any country can contribute positively to national income while political instability reduces it.
Methods of Measuring National Income of a Country
i. Income method: This is obtained by adding incomes received by all the factors of production. The incomes to be added include: workers’ earnings (wages and salary), profit from entrepreneurs, rents on land, interest from capital, etc. However, in order to avoid double counting, transfer payments such as payment to old people, beggars, etc are not included. They are part or people’s incomes which are already counted. The income which is included must be that which arises from the production of goods and services. There must be something given out in return for a payment.
ii. Output method: This method measures the total money value of all goods and services produced in the country in a year. In order to avoid double counting, the figures are collected on the basis of the value added. Value added is defined as the value of output, less cost of input. In this method, national income is measured by adding together the value of the net contributions of the various sectors or enterprises which includes individuals, firms and the government. Output method is also called net product or added value method.
iii. Expenditure method: The expenditure approach calculates the total amount spent on consumption and investment purposes during the year. In other words, it measures the total expenditure on currently produced final goods and services by the individuals or households, firm and government plus net export. Transfer payments such as pensions paid to retired workers, gift to beggars, etc are excluded.
Formula for calculating national income using expenditure method or approach
N. I = C + I + G + X + M + subsidies – Taxes – Depreciation
Where;
N.I = National Income
C = Private consumption expenditure
I = Private investment expenditure
G = Government expenditure on consumption and investment
X = Exports
M = Imports
Worked Example 1
The following is the trading account for Nigeria in the year 1979 (in millions)
(a) Citizen’s private expenditure = #35.0m
(b) Government expenditure on goods and services = #15.6m
(c) Various stocks at home = #11.8m
(d) Exports income from abroad = #13.5m
(e) Imports income paid abroad = #10.4m
(f) Taxes on expenditure = #7.0m
(g) Capital consumption = #5.8m
(h) General subsidies = #1.3m
From the information given above,
i. Calculate the national income for Nigeria for the year 1978
Solution
Alternative Method Using The Formula:
Reasons for Measuring National Income
Countries measure their national incomes for various reasons, which include;
i. It shows the standard of living: National income gives an indication of the standard of living of the country through the measure of per capita income.
ii. It determines the growth rate of the economy: National income helps the country to determine the growth rate of the economy.
iii. Contribution to international organisation: The national income figure determines the country’s contribution to international organisations.
iv. For economic policies and planning: The national income estimate is vital for economic policy and planning.
v. It gives pattern of expenditure of households: The national income data gives an idea of the pattern of expenditure of households.
vi. Performance of the various sectors of the economy: Measured through the output approach, it enables the country to know the performance of the various sectors of the economy.
Problems of Computing National Income
The problems that can be encountered in the measurement and compilation of national income in Nigeria include:
i. Insufficient technical experts: The technical expertise, which is an essential element for collecting and analysing data, is insufficient.
ii. Problem of double counting: Some goods can be counted twice and this gives false national income estimates.
iii. Subsistence production: The predominance in the Nigerian economy of subsistence production, e.g farming, tailoring, carpentry, etc makes estimation difficult.
iv. Problems of Inflation: The national income figures can be over or underestimated as a result of inflation or deflation.
v. Inability to quantify some services: Some services are not easily quantified there you affecting the national income estimates, e.g housewive’s services.
vi. Improper valuation of depreciation: National income estimates will be affected by the valuation of depreciation on capital stock.
vii. Ignorance and Illiteracy: High level of illiteracy and ignorance gives incomplete and false estimates for national income accounting.
viii. Illegal transactions: Certain illegal transactions like drug trafficking, peddling, smuggling make computation of national income very difficult
Uses of National Income
The uses or importance of national income data or figures include:
i. Economic planning: National income provides the basic and comprehensive data on the contribution of various sectors of the economy to national output.
ii. Influences foreign investors: It attracts foreign investment to a country, based on the level of its national income, as investors usually seek countries with rich or fast growing market.
iii. Assessment of economic performance: The national income statistics are used in assessing the performance of the economy, in order to know the effectiveness or utilisation of the productive resources.
iv. Measurement of standard of income: It shows the general level and prosperity of the people over a given period of time, usually a year.
v. Redistribution of income: It enables governments to design policies towards redistributing national income and the allocation of resources and revenue among sectors within the nation.
vi. Index for classification: It is used for classifying nations into the developed nations and the developing ones in respect of their standard of living.
vii. Estimation of assets and liabilities: It is also used to estimate the liabilities and assets of nations.
viii. For future forecast: The national income data are used to forecast future rate of economic growth and development.
Limitations of the Usefulness of National Income Statistics
i. Differences in method of computation: The use of different methods of computation of national income by different countries makes it difficult to have a common basis for comparing nations.
ii. Differences in structure of production: Where subsistence production exists, output is more likely to be grossly under-estimated than a country with a market economy.
iii. Changes in population: The size of national income may not itself be a true measure of economic welfare because of changes in population.
iv. Differences in the Internal value money: The differences in the internal value of money make it difficult to compare the standard of living among nations.
v. Differences in priorities: Different countries have different priorities in terms of expenditure on output and this makes it difficult to compare nations in terms of standard of living.
vi. Changes in the value of money: This makes it difficult to compare national income between years and between nations.
vii. Differences in national needs: Differences in the needs of nations make it difficult for national income comparison.
Cost of Living
Cost of living may be defined as the amount of money an individual spends to obtain the goods and services which will sustain him at a particular time. It is thus the money cost of things as food, shelter, clothing, medical services, etc which the individual consumes.
The cost of living depends largely on the prices of goods and services. If price are high, the cost of living will be high, since the individual will have to spend more money to obtain goods and services. But if the prices are low, less money will be spent, hence the cost of living will be low.
Standard of living
Standard of living may be defined as the level of economic well-being or welfare attained by individual in a country at a particular time. The level of welfare is determined by the quantity and quality of goods and services consumed within a period of time.
The higher the quantity and quality of goods and services consumed, the higher the standard of living and vice versa. The income per head and the distribution of income are used in measuring the standard of living.
Relationship Between Cost Of Living And Standard Of Living
Cost of living, as explained above, largely depends on the prices of goods and services which are consumed. If the prices of goods and services are high, this means an increase in the cost of living since people have to pay more money to get them. If prices increase, people purchase fewer goods and services. They therefore consume less and this results to a fall in their standard of living.
On the other hand, if prices of goods and services fall, people will be able to obtain them in greater amounts. This means a fall in the cost of living. They would also purchase high quality goods and services. This will increase their level of consumption and their standard of living will increase.
In summary, a rise in the cost of living reduces the standard of living, while a reduction in the cost of living increases the standard of living. It is the cost of living that determines the standard of living.
Done studying? See all previous lessons in Economics
Take a quick test for this lesson
i. What do you understand by National Income Accounting
ii. List and explain six concepts of National Income
iii. State five factors that can determine the national income of a country
iv. List and explain three methods of measuring national income
v. Discuss five reasons why National income is measured
vi. State the problems of computing National income
vii. List and explain five uses of National income
viii. Discuss three limitations of the usefulness of national income statistics
ix. Differentiate between cost of living and standard of living
Questions answered correctly? Kudos!!
Do stay connected to itsmyschoollibrary.com for more educational contents.